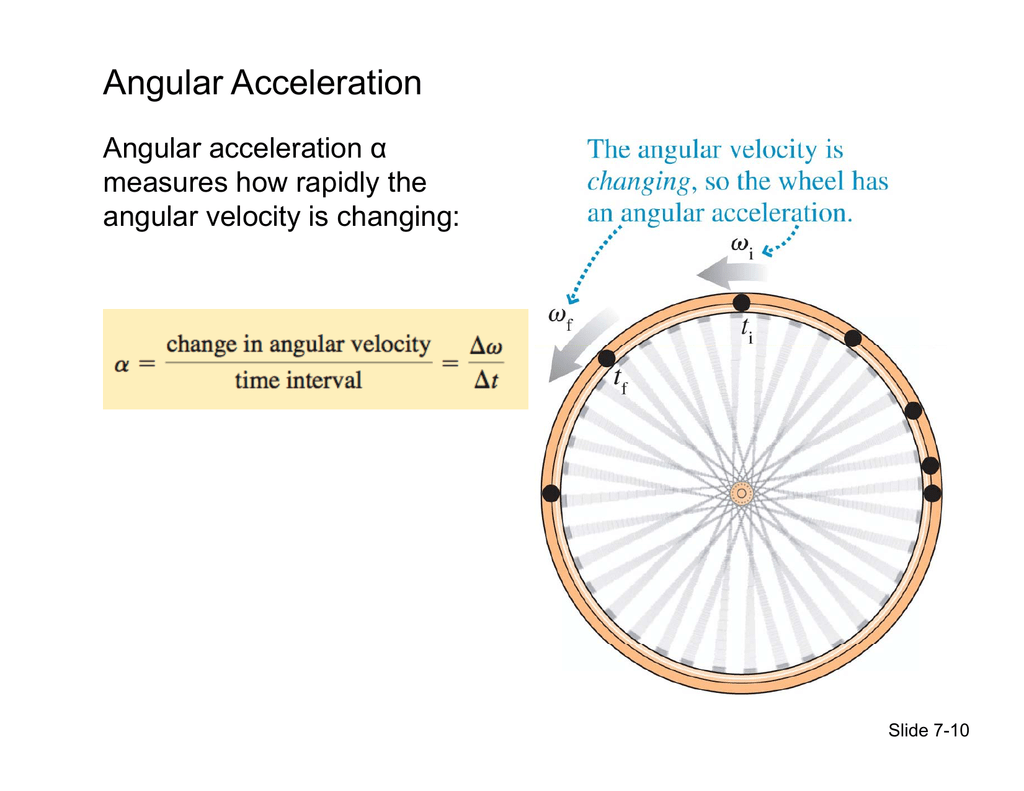
Acceleration Angular Velocity . Angular acceleration α is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. Express your answer in polar coordinates. Let’s first consider the two types of motion with α. In all these cases, there is an angular acceleration, in which ω ω changes. It measures how quickly an. (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? Α = δω δt α = δ ω δ t, where δ ω is the change in. The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration. There are four special cases to consider for the direction of the angular velocity. Determine (a) the angular velocity vector, and (b) the velocity vector. The angular acceleration is also known as rotational acceleration. In rotational dynamics, angular or rotational acceleration is the time rate of change of angular velocity. (d) what is the direction of the angular velocity for 1. It is a quantitative expression of the change in angular velocity per unit time. When the angular velocity is constant, the angular acceleration is zero.
from www.animalia-life.club
Angular acceleration α is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. (d) what is the direction of the angular velocity for 1. Α = δω δt α = δ ω δ t, where δ ω is the change in. Express your answer in polar coordinates. It measures how quickly an. There are four special cases to consider for the direction of the angular velocity. In rotational dynamics, angular or rotational acceleration is the time rate of change of angular velocity. In all these cases, there is an angular acceleration, in which ω ω changes. It is a quantitative expression of the change in angular velocity per unit time. When the angular velocity is constant, the angular acceleration is zero.
Angular Acceleration Examples
Acceleration Angular Velocity When the angular velocity is constant, the angular acceleration is zero. In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows: It measures how quickly an. Let’s first consider the two types of motion with α. When the angular velocity is constant, the angular acceleration is zero. (d) what is the direction of the angular velocity for 1. Α = δω δt α = δ ω δ t, where δ ω is the change in. Express your answer in polar coordinates. Angular acceleration α is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. It is a quantitative expression of the change in angular velocity per unit time. In all these cases, there is an angular acceleration, in which ω ω changes. (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? Determine (a) the angular velocity vector, and (b) the velocity vector. The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration. In rotational dynamics, angular or rotational acceleration is the time rate of change of angular velocity. There are four special cases to consider for the direction of the angular velocity.
From theeducationlife.com
Angular velocity formula Explained The Education Acceleration Angular Velocity Angular acceleration α is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. When the angular velocity is constant, the angular acceleration is zero. Α = δω δt α = δ ω δ t, where δ ω is the change in. There are four special cases to consider for the direction of the angular velocity. The faster the change occurs,. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From majandavid.com
Conversion Of Angular Velocity To Linear Velocity Conversion Chart Acceleration Angular Velocity The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration. Α = δω δt α = δ ω δ t, where δ ω is the change in. When the angular velocity is constant, the angular acceleration is zero. (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? It is a quantitative expression of the change in angular velocity per. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From studylib.net
Circular Motion Tangential & Angular Acceleration θ Acceleration Angular Velocity There are four special cases to consider for the direction of the angular velocity. In rotational dynamics, angular or rotational acceleration is the time rate of change of angular velocity. In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows: (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? When the angular velocity is constant, the angular acceleration is zero.. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.animalia-life.club
Angular Acceleration Examples Acceleration Angular Velocity Angular acceleration α is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. It is a quantitative expression of the change in angular velocity per unit time. It measures how quickly an. In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows: When the angular velocity is constant, the angular acceleration is zero. The angular acceleration is also known as rotational. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 13 Rotation of a Rigid Body PowerPoint Presentation, free Acceleration Angular Velocity The angular acceleration is also known as rotational acceleration. It is a quantitative expression of the change in angular velocity per unit time. Angular acceleration α is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. In all these cases, there is an angular acceleration, in which ω ω changes. In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows: It. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Angular Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID5167370 Acceleration Angular Velocity In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows: Determine (a) the angular velocity vector, and (b) the velocity vector. There are four special cases to consider for the direction of the angular velocity. The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration. (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? Α = δω δt α =. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From sciencequery.com
Formula for angular acceleration Science Query Acceleration Angular Velocity There are four special cases to consider for the direction of the angular velocity. In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows: (d) what is the direction of the angular velocity for 1. Angular acceleration α is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. The angular acceleration is also known as rotational acceleration. Express your answer in. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Angular Position, Velocity and Acceleration PowerPoint Acceleration Angular Velocity Α = δω δt α = δ ω δ t, where δ ω is the change in. In rotational dynamics, angular or rotational acceleration is the time rate of change of angular velocity. The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration. In all these cases, there is an angular acceleration, in which ω ω changes. In equation form,. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.piping-designer.com
Instantaneous Angular Acceleration Acceleration Angular Velocity Let’s first consider the two types of motion with α. The angular acceleration is also known as rotational acceleration. In rotational dynamics, angular or rotational acceleration is the time rate of change of angular velocity. Angular acceleration α is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. (d) what is the direction of the angular velocity for 1. Express. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT PHYS 1441 Section 001 Lecture 16 PowerPoint Presentation, free Acceleration Angular Velocity The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration. It measures how quickly an. Α = δω δt α = δ ω δ t, where δ ω is the change in. In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows: Determine (a) the angular velocity vector, and (b) the velocity vector. (d) what is the direction of the angular. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.physicsbootcamp.org
Rotational Acceleration Acceleration Angular Velocity In all these cases, there is an angular acceleration, in which ω ω changes. Α = δω δt α = δ ω δ t, where δ ω is the change in. (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows: The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration.. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter Eight PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1801340 Acceleration Angular Velocity Angular acceleration α is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. Express your answer in polar coordinates. When the angular velocity is constant, the angular acceleration is zero. The angular acceleration is also known as rotational acceleration. There are four special cases to consider for the direction of the angular velocity. In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Mechanics. PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2098717 Acceleration Angular Velocity (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? Express your answer in polar coordinates. When the angular velocity is constant, the angular acceleration is zero. It is a quantitative expression of the change in angular velocity per unit time. Determine (a) the angular velocity vector, and (b) the velocity vector. In all these cases, there is an angular. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter Eight PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1926367 Acceleration Angular Velocity When the angular velocity is constant, the angular acceleration is zero. The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration. In equation form, angular acceleration is expressed as follows: Express your answer in polar coordinates. Let’s first consider the two types of motion with α. (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? (d) what is the. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.animalia-life.club
Velocity Acceleration Formula Acceleration Angular Velocity (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? In all these cases, there is an angular acceleration, in which ω ω changes. Express your answer in polar coordinates. Α = δω δt α = δ ω δ t, where δ ω is the change in. The faster the change occurs, the greater the angular acceleration. (d) what is. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Rotational Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6012787 Acceleration Angular Velocity When the angular velocity is constant, the angular acceleration is zero. The angular acceleration is also known as rotational acceleration. It measures how quickly an. Angular acceleration α is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. There are four special cases to consider for the direction of the angular velocity. Α = δω δt α = δ ω. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.thestructuralengineer.info
Calculation Example Angular acceleration, angular velocity Acceleration Angular Velocity Express your answer in polar coordinates. Angular acceleration α is defined as the rate of change of angular velocity. It measures how quickly an. There are four special cases to consider for the direction of the angular velocity. The angular acceleration is also known as rotational acceleration. (d) what is the direction of the angular velocity for 1. Α =. Acceleration Angular Velocity.
From www.sciencefacts.net
Angular Acceleration Definition, Formula, & Example Problems Acceleration Angular Velocity Α = δω δt α = δ ω δ t, where δ ω is the change in. Express your answer in polar coordinates. There are four special cases to consider for the direction of the angular velocity. (c) at what time, \(t=t_{1}\) is the angular velocity zero? (d) what is the direction of the angular velocity for 1. When the. Acceleration Angular Velocity.